Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is a powerful way to care for patients between clinic visits. But for RPM to work, patients must consistently use their monitoring devices and share accurate data. Many patients stop using devices after the first few days or don’t use them the right way. That’s where adherence becomes critical.
In this blog, we’ll explain how to increase patient adherence in remote monitoring in 2025 using practical strategies based on stats and data. Whether you’re monitoring blood pressure, glucose levels, or post-surgical recovery, improving adherence helps you catch problems early, reduce hospital readmissions, and improve long-term outcomes.
You’ll learn why patients drop off, how to improve patient compliance and engagement in 2025, and how to build a workflow your clinic can follow. Let’s start with the real impact patient adherence can have.
Table of Contents
Why is Patient Adherence Important in Remote Monitoring?
When patients stick to their remote monitoring routines, like checking their blood pressure daily or using a connected glucose meter, the data helps doctors make faster, better decisions. But when patients miss readings or stop using the devices altogether, it limits the effectiveness of RPM programs.
Here’s What Studies Show About the Importance of Patient Adherence in Remote Monitoring
One national evaluation, published in the NIH’s National Library of Medicine, looked at remote monitoring (RM) adherence across 26 Veterans Health Administration (VHA) facilities, covering about 15,000 patients with cardiac devices. Adherence levels varied widely, ranging from 46% to 96% depending on the clinic.
- 53.8% of clinicians said RM adherence was extremely important for improving patient outcomes, while 34.6% rated it as very important, and *11.5% as important.
- Clinics with higher adherence rates spent twice as much time managing remote monitoring (9.1 hours/week vs. 4.5 hours/week).
- These high-performing clinics focused on clear patient education, standard workflows for nonadherence, and consistent follow-ups via phone and mail (NIH Study – PMC10774668).
In another case, the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center found that their RPM program led to a 76% reduction in 30-day readmissions for Medicare patients using Vivify Health monitoring tools
RPM isn’t just about collecting numbers. It’s about turning those numbers into care decisions, and that only works if patients stay consistent. That’s why improving adherence is central to the success of any remote monitoring program in 2025.
Top Reasons for Low Patient Adherence in Remote Monitoring Programs
Even with the best devices and support, many patients stop using remote monitoring tools after a few days or weeks. To improve patients outcomes, it’s important to understand what’s getting in the way of consistent use. These are the most common reasons for low patient adherence in remote monitoring programs:
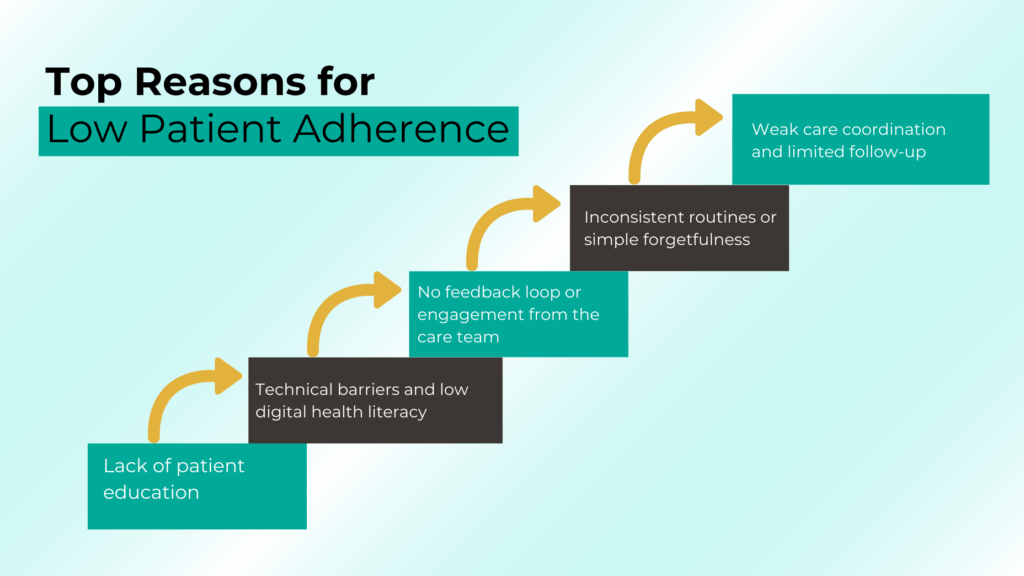
- Lack of patient education
- Technical barriers and low digital health literacy
- No feedback loop or engagement from the care team
- Inconsistent routines or simple forgetfulness
- Weak care coordination and limited follow-up
Here is the brief overview of each reason for patient non-compliance in remote patient monitoring.
1. Lack of Patient Education
Many patients don’t fully understand why they’re using a remote monitoring device or how their readings impact care. Without clear, ongoing education, RPM can feel like a burden. Studies show that high-performing clinics prioritize patient education from the start, and consistently reinforce it throughout the care plan.
2. Technical Barriers and Low Digital Health Literacy
For patients who aren’t comfortable with technology, even simple tasks like syncing a device or charging a monitor can feel overwhelming. This is especially true for older adults. Without technical support or training, these patients are more likely to drop off. Improving digital health literacy is key to improving long-term adherence.
3. No Feedback Loop or Engagement from the Care Team
When patients send daily readings but never hear back, they start to wonder if it matters. This lack of a feedback loop lowers motivation. Patients need to know that someone is watching and that their data is helping shape their care. Active patient engagement, even through a short message or monthly check-in, makes a big difference.
4. Inconsistent Routines or Simple Forgetfulness
Remote health tracking only works if it becomes part of the patient’s daily routine. But many patients struggle to remember their readings, especially when managing multiple health issues or busy schedules. Without reminders or reinforcement, patient compliance fades quickly.
5. Weak Care Coordination and Limited Follow-up
Low adherence is often linked to poor care coordination. In the NIH-backed study of VHA clinics, facilities with structured workflows, defined staff roles, and regular follow-ups had significantly higher adherence rates. On the other hand, clinics that didn’t follow up regularly, especially after a missed reading, struggled to keep patients on track.
How to Improve Patient Adherence in Remote Monitoring?
Improving patient adherence in remote monitoring isn’t about adding more devices. It’s about creating a process that helps patients stay consistent. Based on NIH-backed research and practical strategies from high-performing clinics, here are the most effective ways to improve adherence and long-term patient engagement in 2025.
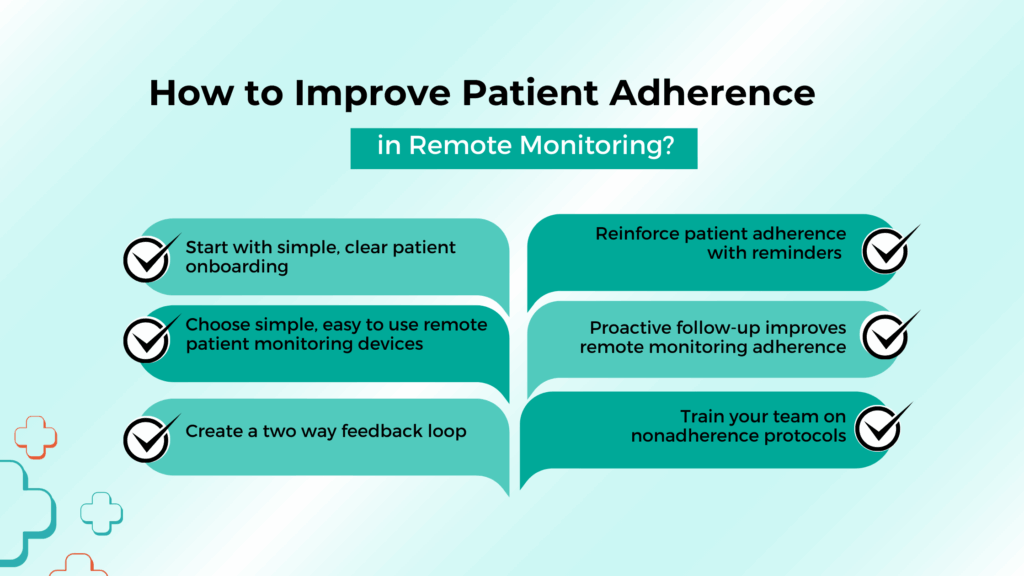
- Start with simple, clear patient onboarding
- Choose simple, easy to use remote patient monitoring devices
- Create a two way feedback loop
- Reinforce patient adherence with reminders
- Proactive follow-up improves remote monitoring adherence
- Train your team on nonadherence protocols
Look below for a detailed overview of these strategies to improve patient engagement in remote patient monitoring.
1. Start with Simple, Clear Patient Onboarding
Many patients lose confidence right at the beginning. That’s why onboarding needs to be simple, supportive, and repeatable. Explain the purpose of the device, how often it should be used, and, most importantly, how their data helps shape care decisions.
- Use checklists, printed guides, or short how-to videos.
- Make sure to cover both device setup and what to expect next.
- Consider using a nurse or care manager to reinforce education after the first visit.
This first step builds digital health confidence and sets the tone for long-term patient adherence.
2. Choose Simple, Easy to Use Remote Monitoring Devices
To keep patients engaged, monitoring tasks should be as easy as brushing their teeth. Choose devices that are simple to use (one-button use or auto-syncing), comfortable to wear (if wearable) or Integrated with reminders via SMS, app alerts, or email.
The easier it is to use, the less likely patients are to skip it. Look for tools designed with usability and accessibility in mind, especially for older or low-tech patients.
Related Article: A Comprehensive Guide to Remote Patient Monitoring Devices
3. Create a Two-Way Feedback Loop
Patients need to know their readings matter. When they get a message like, “Great job keeping your BP under 130 this week,” it reinforces behavior.
- Use automated messages when readings are on target.
- Set alerts for your staff to follow up when readings are out of range or missing.
- Make it a feedback loop, not just data collection.
This improves patient engagement and prevents the “I guess no one is looking at my data” drop-off.
4. Reinforce Patient Adherence with Reminders
Sometimes patients simply forget. Use a combination of daily SMS or push notifications, weekly “wrap-up” reports showing trends. Consider involving family members when appropriate, especially in elderly care.
Helping patients create a routine increases consistency and reinforces treatment adherence. When RPM becomes part of their normal day, results improve.
5. Proactive Follow-Up Improves Remote Monitoring Adherence
Don’t wait until the patient stops sending data. Build care coordination into your RPM process:
- Schedule biweekly check-ins via phone or video.
- Address technical issues early. Don’t assume they’ll figure it out.
- Recognize effort: “Thanks for submitting your readings every day this week.”
Clinics that do this see far better compliance with remote monitoring and fewer gaps in care.
6. Train Your Team on Nonadherence Protocols
The NIH study found that clinics with standardized workflows for nonadherence had higher success rates. That means you must have a system to flag missed readings, assign clear roles to staff members and document each outreach attempt.
RPM Programs like CandiHealth offer centralized dashboard with structured workflow. You can assign roles to staff, set customized alerts based on patients needs and get notifications if patients miss readings.
Conclusion: Bringing It All Together to Improve Patient Adherence
The studies are clear: when patients stay engaged, RPM programs reduce hospital visits, improve chronic disease control, and support faster care decisions. But without adherence, even the best devices lose their value.
Here’s what matters most:
- Educate patients clearly from day one. Don’t assume they understand the purpose of RPM.
- Choose user-friendly tools that fit into daily life. Technical simplicity increases consistency.
- Create a two-way feedback loop. Let patients know their data is being seen and used.
- Assign roles and build a system for monitoring, follow-up, and data review.
- Use adherence metrics to refine and improve your program over time.
By taking a structured and patient-centered approach, as offered by the CandiHealth platform, your clinic can turn remote monitoring into a meaningful part of care.
Related Articles
A Comprehensive Guide to Remote Patient Monitoring Devices
What is Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) and How It’s Transforming Chronic Care
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the meaning of patient compliance or adherence?
Patient compliance refers to how well a patient follows a healthcare provider’s recommended treatment plan, including taking medications, attending appointments, and using prescribed devices.
While “compliance” is still used, many healthcare providers now prefer the term “adherence” because it emphasizes the patient’s active role in managing their own care, rather than simply following orders.
2. What is RPM used to monitor patients for?
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is used to track patients’ health data from home using digital devices. It commonly monitors conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, heart disease, COPD, and post-surgical recovery. RPM allows clinicians to get real-time insights into vital signs like blood pressure, glucose levels, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and weight, without requiring an in-person visit.
3. What are the ethical considerations of RPM?
Ethical considerations in RPM include:
- Patient privacy: Ensuring personal health data is securely transmitted and stored.
- Informed consent: Patients should fully understand how their data will be used.
- Data access: Only authorized medical professionals should access RPM data.
- Health equity: RPM should be accessible to patients regardless of age, tech literacy, or income level.
Clinics must follow HIPAA and CMS guidelines to protect patient rights and data security in all RPM programs.
4. How does RPM improve medication adherence?
RPM improves medication adherence by providing regular data and feedback that helps patients stay accountable. For example, if a patient’s blood pressure remains high, the care team can check if medications are being taken correctly and intervene early.
Many RPM platforms also send reminders or alerts tied to medication schedules, which reinforces daily compliance and prevents gaps in treatment.
5. What advantages does RPM offer in monitoring medication adherence?
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) helps track medication adherence by providing real-time health data, such as blood pressure or glucose levels, that reflect how well a patient is responding to treatment.
RPM platforms can also send reminders for medication schedules, alert providers when readings are off, and support early interventions, all of which help improve medication consistency and overall treatment effectiveness.